React state
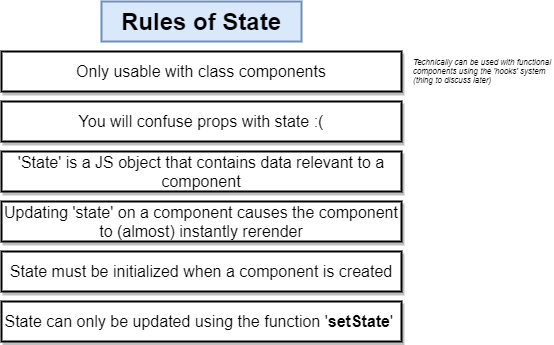
Example:
initialize State and update with setState.
class App extends React.Component{
// First function ever called when an instance of this class is created
constructor (props) {
//all the Code of Rect.component should still be called
super(props);
// intialize state
// ONLY TIME where we do direct assignemnt to this.state
this.state={lat:null, errorMessage:''};
window.navigator.geolocation.getCurrentPosition(
(position)=>{
this.setState({lat:position.coords.latitude});
},
(err)=>{
this.setState({errorMessage:'Cannot show the Geolocation'})
}
);
}
// Must Have: Define Render method to return jsx
render() {
if(this.state.errorMessage && !this.state.lat){
return <div>
Error:{this.state.errorMessage}
</div>
}
if (!this.state.errorMessage && this.state.lat){
return <div>
Latitude:{this.state.lat}
</div>
}
return <div>Loading!</div>
}
}
Alternative Way of Initialize the state instead of using the constructor:
class App extends React.Component{
state={lat:null, errorMessage:''}
componentDidMount(){
console.log('My component was rendered to the screen');
window.navigator.geolocation.getCurrentPosition(
(position)=>{
this.setState({lat:position.coords.latitude});
},
(err)=>{
this.setState({errorMessage:'Cannot show the Geolocation'})
}
);
}
// Must Have: Define Render method to return jsx
render() {
if(this.state.errorMessage && !this.state.lat){
return <div>
Error:{this.state.errorMessage}
</div>
}
if (!this.state.errorMessage && this.state.lat){
return <div>
Latitude:{this.state.lat}
</div>
}
return <div>Loading!</div>
}
}