Asynchronous Code, Callbacks & Promises
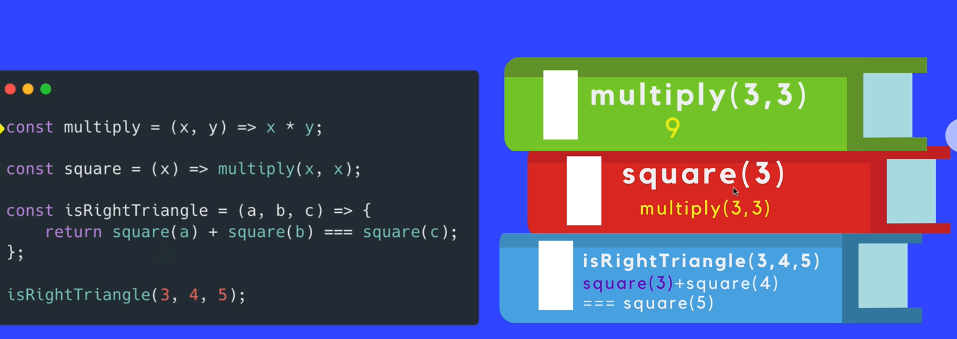
Call Stack
The mechanism the JS interpreter uses to keep track of its place in a script that calls multiple functions.
How JS “knows” what function is currently being run and what functions are called from within that function etc.
Example: If you read a book the “Call Stack” represents your finger which is keeping track of the line you are currently reading.
How it works

-
When a script calls a function, the interpreter adds it to the call stack and then starts carrying out the function
-
Any functions that are called by that function are added to the call stack further up, and run where their calls are reached.
-
When the current function is finished, the interpreter takes it off the stack and resumes execution where it left off in the last code listing.
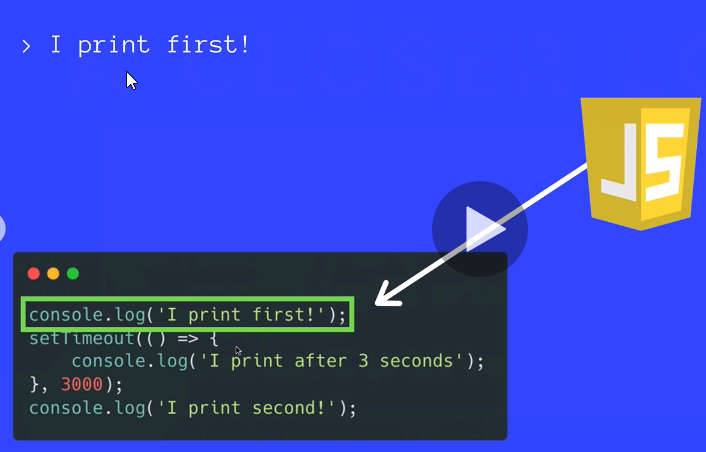
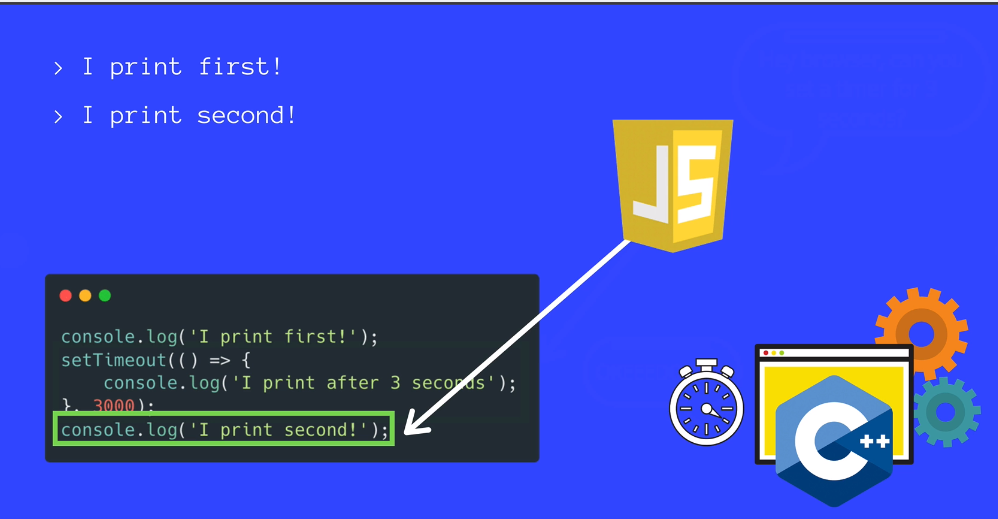
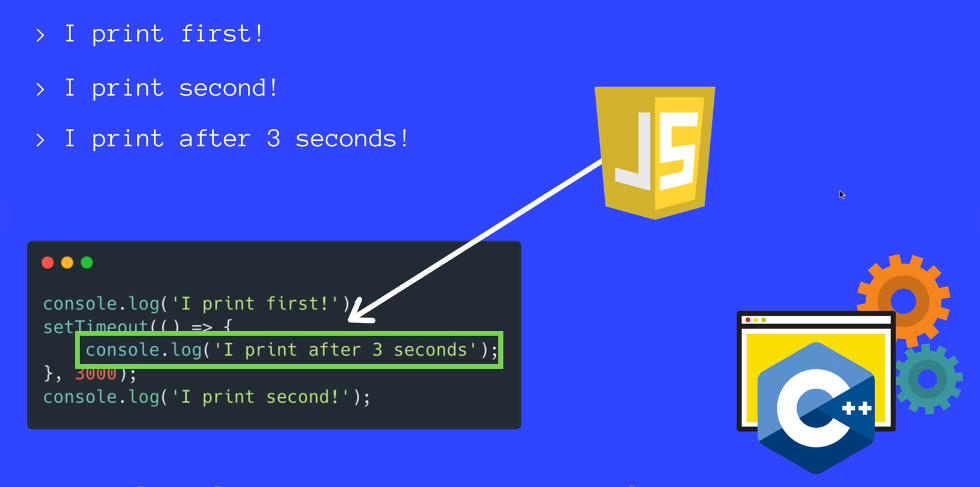
JavaScript is a Single Threaded Language
At any given point in time, that single JavaScript thread is running at most one line of JavaScript code.
How Asynchronous Callbacks work
-
Browser come with Web APIs that are able to handle certain tasks in the background /like making requests or setTimeout)
-
The Js call stack recognizes these Web API functions and passes them off to the browser to take care of
-
Once the browser finishes those tasks, the yretunr and are pushed onto the stack as a callback.


Example for Callbacks where we see that it can sometimes be a real pain:
A moving button whit a success and failure callback
button {
font-size: 50px;
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="app.css">
<title>Callback Hell</title>
</head>
<body>
<h4>Try shrinking your window and see what happens!</h4>
<button>Move Me!</button>
<script src="app.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
const btn = document.querySelector('button');
// setTimeout(()=>{
// btn.style.transform=`translateX(100px)`;
// setTimeout(()=>{
// btn.style.transform=`translateX(200px)`;
// setTimeout(()=>{
// btn.style.transform=`translateX(100px)`;
// },1000);
// },1000);
// },1000);
//-> in short:
const moveX=(element,amount,delay,onSuccess,onFailure)=>{
setTimeout(()=>{
const bodyBoundary= document.body.clientWidth;
const elementRight=element.getBoundingClientRect().right;
const currLeft=element.getBoundingClientRect().left;
if(elementRight+amount>bodyBoundary){
onFailure();
}
else{
element.style.transform=`translateX(${currLeft+amount}px)`;
onSuccess();
}
},delay)
};
// moveX(btn, 100, 2000, () => {
// moveX(btn, 100, 1000, () => {
// moveX(btn, 100, 1000, () => {
// moveX(btn, 100, 1000, () => {
// moveX(btn, 100, 1000)
// })
// })
// })
// })
moveX(btn,100,1000,()=>{
//success
moveX(btn,400,1000,()=>{
//success
moveX(btn,800,1000,()=>{
},
//fail
()=>{
alert("CAnnot move further3")
})
},
//fail
()=>{alert("CAnnot move further1")})
},
//fail
()=>{
alert("CAnnot move further2")
})
Introducing to Promises
A Promise is an object representing the eventual completion or failure of an asynchronous operation.
When working with promises there are two things we need to understand:
- How we create promises or how we create a function that returns a promise.
- How to consume ore interact with promises.
A promise is a returned object to which you attach callbacks, instead of passing callbacks into a function.
const willGetYouADog = new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{
//resolves the promise:
//resolve()
//rejects the promise:
//reject()
const rand = Math.random();
if (rand<0.5) resolve()
else reject()
})
//The `Then` paramater is used to define the action which should happen, when the promise is resolved!
willGetYouADog.then(()=>{
console.log('We got a dog')
}).catch() //.catch runs when it gets rejected
//you could also write
willGetYouADog.catch(()=>console.log('No Dog'))
Returning Promises from Functions
const makeDogPromise = () => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
const rand = Math.random();
if (rand < 0.5) {
resolve();
}
else {
reject();
}
}, 5000);
});
};
makeDogPromise()
.then(() => {
console.log('YAY WE GOT A DOG!!!!');
})
.catch(() => {
console.log(':( NO DOG');
});
Resolving/Rejecting with Values
//This is a FAKE Http Request Function
//It takes 1 second to resolve or reject the promise, depending on the url that is passed in
const fakeRequest = (url) => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
const pages = {
'/users' : [
{ id: 1, username: 'Bilbo' },
{ id: 5, username: 'Esmerelda' }
],
'/about' : 'This is the about page!'
};
const data = pages[url];
if (data) {
resolve({ status: 200, data }); //resolve with a value!
}
else {
reject({ status: 404 }); //reject with a value!
}
}, 1000);
});
};
//this should resolve
fakeRequest('/users')
.then((res) => {
console.log('Status Code', res.status);
console.log('Data', res.data);
console.log('REQUEST WORKED!');
})
.catch((res) => {
console.log(res.status);
console.log('REQUEST FAILED');
});
//THIS should reject
fakeRequest('/dogs')
.then((res) => {
console.log('Status Code', res.status);
console.log('Data', res.data);
console.log('REQUEST WORKED!');
})
.catch((res) => {
console.log(res.status);
console.log('REQUEST FAILED');
});
Promise Chaining
//This is a FAKE Http Request Function
//It takes 1 second to resolve or reject the promise, depending on the url that is passed in
const fakeRequest = (url) => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
const pages = {
'/users' : [
{ id: 1, username: 'Bilbo' },
{ id: 5, username: 'Esmerelda' }
],
'/users/1' : {
id : 1,
username : 'Bilbo',
upvotes : 360,
city : 'Lisbon',
topPostId : 454321
},
'/users/5' : {
id : 5,
username : 'Esmerelda',
upvotes : 571,
city : 'Honolulu'
},
'/posts/454321' : {
id : 454321,
title :
'Ladies & Gentlemen, may I introduce my pet pig, Hamlet'
},
'/about' : 'This is the about page!'
};
const data = pages[url];
if (data) {
resolve({ status: 200, data }); //resolve with a value!
}
else {
reject({ status: 404 }); //reject with a value!
}
}, 1000);
});
};
fakeRequest('/users')
.then((res) => {
console.log(res);
const id = res.data[0].id;
//take output from request and make new request
return fakeRequest(`/users/${id}`);
})
.then((res) => {
console.log(res);
const postId = res.data.topPostId;
return fakeRequest(`/posts/${postId}`);
})
.then((res) => {
console.log(res);
})
.catch((err) => {
console.log('OH NO!', err);
});
// ************************************************
// ATTEMPT 2 (deliberate error to illustrate CATCH)
// ************************************************
// fakeRequest('/users')
// .then((res) => {
// console.log(res);
// const id = res.data[0].id;
// return fakeRequest(`/useALSKDJrs/${id}`); //INVALID URL, CATCH WILL RUN!
// })
// .then((res) => {
// console.log(res);
// const postId = res.data.topPostId;
// return fakeRequest(`/posts/${postId}`);
// })
// .then((res) => {
// console.log(res);
// })
// .catch((err) => {
// console.log('OH NO!', err);
// });
Refactoring Callback example with Promises
button {
font-size: 50px;
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="app.css">
<title>Refactoring With Promises</title>
</head>
<body>
<h4>Try shrinking your window and see what happens!</h4>
<button>Move Me!</button>
<script src="app.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
const moveX = (element, amount, delay) => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
const bodyBoundary = document.body.clientWidth;
const elRight = element.getBoundingClientRect().right;
const currLeft = element.getBoundingClientRect().left;
if (elRight + amount > bodyBoundary) {
reject({ bodyBoundary, elRight, amount });
}
else {
element.style.transform = `translateX(${currLeft + amount}px)`;
resolve();
}
}, delay);
});
};
const btn = document.querySelector('button');
moveX(btn, 100, 1000)
.then(() => moveX(btn, 100, 1000))
.then(() => moveX(btn, 100, 1000))
.then(() => moveX(btn, 100, 1000))
.then(() => moveX(btn, 100, 1000))
.then(() => moveX(btn, 100, 1000))
.then(() => moveX(btn, 100, 1000))
.then(() => moveX(btn, 100, 1000))
.then(() => moveX(btn, 100, 1000))
.then(() => moveX(btn, 100, 1000))
.then(() => moveX(btn, 100, 1000))
.then(() => moveX(btn, 100, 1000))
.then(() => moveX(btn, 100, 1000))
.then(() => moveX(btn, 100, 1000))
.then(() => moveX(btn, 100, 1000))
.then(() => moveX(btn, 100, 1000))
.catch(({ bodyBoundary, amount, elRight }) => {
console.log(`Cannot Move! Body is ${bodyBoundary}px wide`);
console.log(`Element is at ${elRight}px, ${amount}px is too large!`);
});
//This function moves an element "amount" number of pixels after a delay.
//If the element will stay on screen, we move the element and call the onSuccess callback function
//If the element will move off screen, we do not move the element and instead call the onFailure callback
// const moveX = (element, amount, delay, onSuccess, onFailure) => {
// setTimeout(() => {
// const bodyBoundary = document.body.clientWidth;
// const elRight = element.getBoundingClientRect().right;
// const currLeft = element.getBoundingClientRect().left;
// if (elRight + amount > bodyBoundary) {
// onFailure();
// }
// else {
// element.style.transform = `translateX(${currLeft + amount}px)`;
// onSuccess();
// }
// }, delay);
// };
// LOOK AT THIS UGLY MESS!
// moveX(
// btn,
// 300,
// 1000,
// () => {
// //success callback
// moveX(
// btn,
// 300,
// 1000,
// () => {
// //success callback
// moveX(
// btn,
// 300,
// 1000,
// () => {
// //success callback
// moveX(
// btn,
// 300,
// 1000,
// () => {
// //success callback
// moveX(
// btn,
// 300,
// 1000,
// () => {
// //success callback
// alert('YOU HAVE A WIDE SCREEN!');
// },
// () => {
// //failure callback
// alert('CANNOT MOVE FURTHER!');
// }
// );
// },
// () => {
// //failure callback
// alert('CANNOT MOVE FURTHER!');
// }
// );
// },
// () => {
// //failure callback
// alert('CANNOT MOVE FURTHER!');
// }
// );
// },
// () => {
// //failure callback
// alert('CANNOT MOVE FURTHER!');
// }
// );
// },
// () => {
// //failure callback
// alert('CANNOT MOVE FURTHER!');
// }
// );